
> print -dpng 'myPlot. > ylabel('value') % - Add labels, legend and title > plot(t,y2,'r') % Add to graph with cos plot in red > hold on % Says to wait with plot instead of overwriting > % DRAW SIN AND COS CURVE ON SAME GRAPH: > plot(t,y1) % Show nice sin curve in default blue. > sum(sum(A)) % Sums all elements in A and would return (27). > sum(a) % Adds all elements in a and returns (17.5). % Where: c = col, r = row of any value >= 7. > r,c = find(A>=7) % Finds the row, column index of all values >= 7. > A = magic(3) % 3x3 matrix where all cols up to same value. % WARNING: if matrix does max for each column. > val = max % Returns (3) max value in v. > exp(v) % " " " " " " base e exponentiaion * B % element-wise multiplication (must be same dimensions) > A * C % matrix multiplication (results is 3x2 matrix) > v = % NOTE: commas behave same as semicolons
#GNU OCTAVE CODE#

#GNU OCTAVE INSTALL#
If you install Octave you can copy and paste these commands to see the full output from each line.
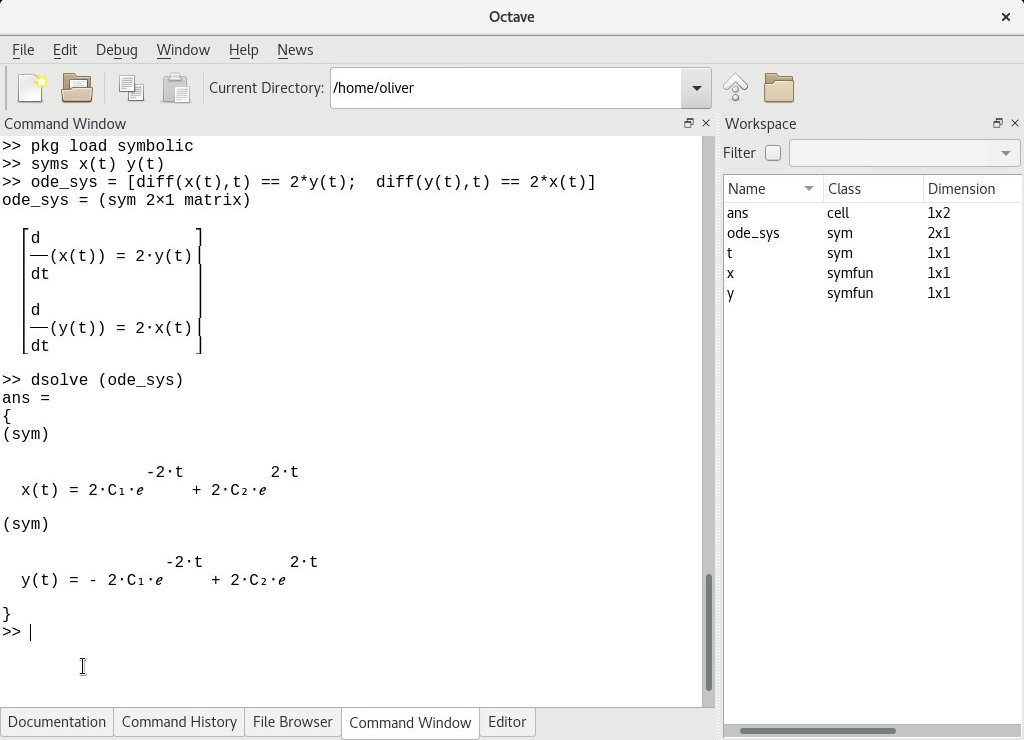
Often I'll explain output in the % comments, but generally I have saved space by not showing any output lines. Here I go through some commands - roughly in the order I saw them in the online machine learning course.
#GNU OCTAVE WINDOWS#
It works on all platforms, although on windows you will need to install it with Cygwin. Octave is an excellent language to prototype machine learning. Most of them I actually saw in an excellent online machine learning course which is referenced and acknowledged properly below, and was my reason for learning Octave. This page is my own "cheat sheet" where I list out most of the commands I'll need.
#GNU OCTAVE FREE#
The language is very similar to and *mostly* comaptible with MATLAB - but unlike Matlab is free and open source under a GNU General Public License. It provides its own command line interface for solving linear and nonlinear problems and plotting graphs. Octave-gtk a GTK+ binding for GNU/Octave.GNU Octave is a high-level programming language, primarily intended for numerical computations, and very useful for matrix operations. sudo checkinstallĪlternatively, you can just sudo make install.Īrticles by Barry O'Donovan Some introductory articles. Debian package versions must have numbers in them. checkinstall will complain loudly about a bad version number. checkinstall is a program to automatically make a debian package, so it is easy to uninstall or install on similar systems. Mouse support in interactive terminals: yes Look for the following lines: X Window System terminal: yes The output of configure will tell you if you have the correct things enabled in gnuplot. Run the cvs commands from 's instructions: cvs login You will need at least these packages (please add to this list if you see the need for more): sudo aptitude install build-essential cvs autoconf automake libgd2-xpm-dev checkinstall xorg-dev
These instructions are for 8.04 hopefully it will make it into the 8.10 or 9.04 repos.īuild GNUPlot with the instructions at. For certain tasks, this is obviously a huge improvement over using xlim() and ylim(). The latest GNUPlot from CVS ( is what I used) can zoom with the mouse. To run octave open a terminal and type octave Octave is in the Ubuntu universe and can be installed with synaptic or apt-get. A list of commands can be put into a file and executed as an interpreted scripting language.Ī simple example of a Octave session octave:1> a = 2 * 3 It gives you an command line environment where you can do calculation, solve equations, manipulate matrices and plot graphs. It is free software, and it is similar to the commercial product MATLAB. GNU Octave is a high-level language, primarily intended for numerical computations.

This article is incomplete, and needs to be expanded.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
